Gas Chromatograph mass spectrometer coupled with autosampler for headspace analysis
Shimadzu QP-2010 Autosampler HDA
Name of the contact point Rosamaria Capuano (capuano@ing.uniroma2.it) Name of the laboratory: Centro Interdipartimentale per la volatolomica

Description of the technique
Gas chromatograph with mass spectrometry detection. Coupled with a autosampler with controlled temperature. Direct injection or SPME enabled
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Column Flow Up to 4 mL/min and Variety of Column Selection
Analytical Method Transfer Available based on GCMS-QP5000 Series
Enables Direct Sample Injection (DI) and Easy Expandability without Any Changes to the GC
Mode for Lower Running Cost in Laboratory; Power Consumed in Analysis Standby Mode Reduced 40%*
Mass range: m/z 1.5 to 1000
Ionization mode: EI
EI scan sensitivity: 1 pg octafluoronaphthalene m/z 272 S/N > 200 (Installation check out specs) Column flow: Up to 4mL/min
Pump: Turbomolecular pump (58 L/sec for He), Rotary pump 30 L/min (60Hz)
AVAILABLE TECHNIQUES
Headspace analysis
Compatibile with SPME
Automatic sample injection with programmable temperature and flow. Possibility to install an additional column
SAMPLE
Analysis of the headspace of either solid or liquid samples. To enable the use with the autosampler the sample is kept in suitable vials capped with a perforable sept. The manual use is available
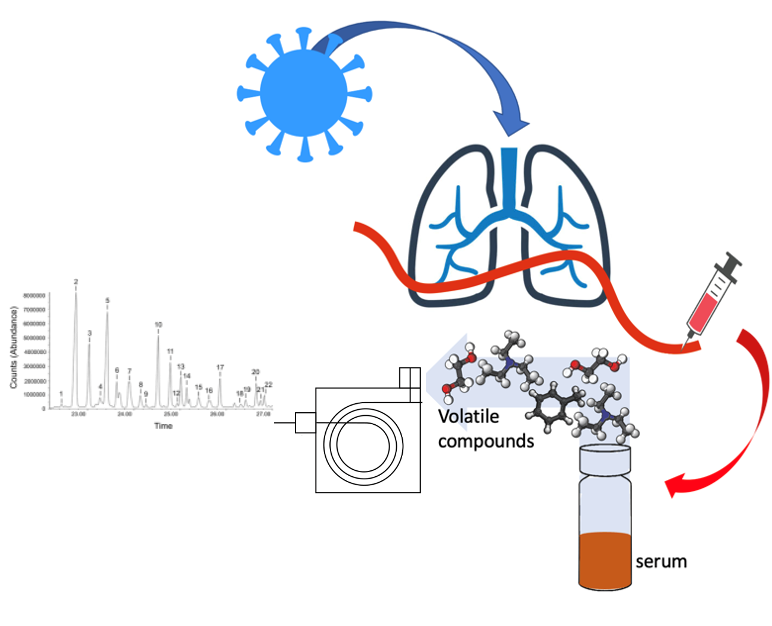
USE FOR: Mainly used for volatolomics analysis. The volatolome is the volatile fraction of the metabolome of biological samples. These may be collected in-vivo (urines, saliva, plasma,…) or in-vitro from cultured cells or microorganisms. The instrument is also used to analyze the volatilome from vegetable samples and food matrices and intermediate products of industrial food processes and beverages.
Case study 1 – Urine analysis for COVID-19 diagnosis-
Analysis of urines samples collected at the university hospital of Rome Tor Vergata from COVID-19 affected individuals and controls.
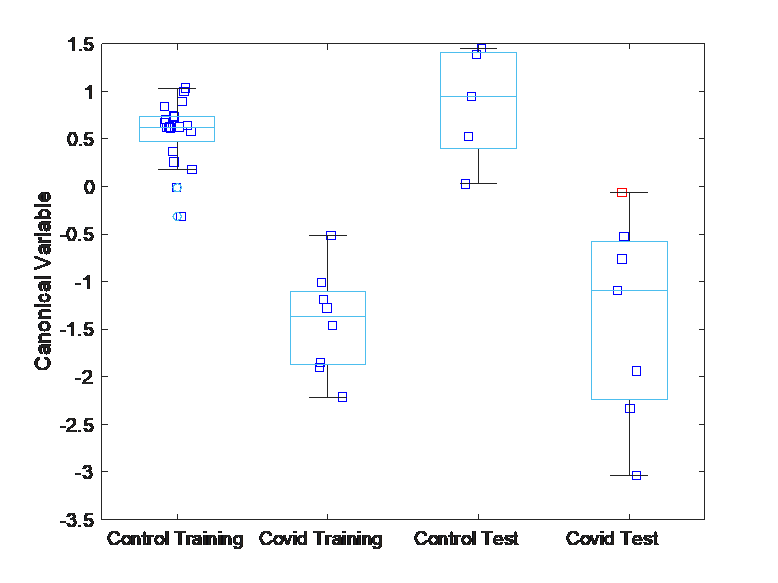
Machine learning analysis of chromatograms enables the identification of the diseases with performance comparable to the traditional analysis.
