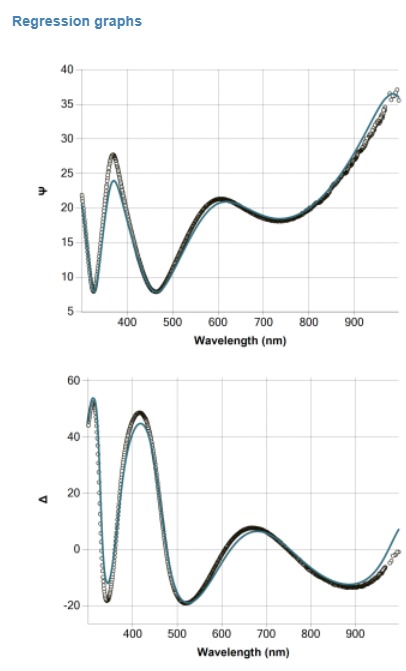
| Description Spectroscopic ellipsometry is a surface-sensitive, non-destructive, non-intrusive optical technique widely used for thin layers and surface characterization. It is based simply on the change in the polarization state of light as it is reflected obliquely from a thin film sample. Depending on the type of material, spectroscopic ellipsometers can measure thickness from a few Å to tens of microns. It is also an excellent technique for multi-layers measurement. Spectroscopic ellipsometry allows a range of thin film properties to be characterized, like layer thickness, optical properties (n,k), optical band gap, interface and roughness thickness, film composition, uniformity by depth and area, and more. Materials suitable for spectroscopic ellipsometry include semiconductors, dielectrics, polymers, organics, and metals. Ellipsometry can also be used to study solid-liquid or liquid-liquid interfaces. |

Francesca Brunetti, francesca.brunetti@uniroma2.it CHOSE-Electronic Engineering Department
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
-Spectral range 370 -1000 nm simultaneously acquiring 390 wavelengths via Silicon CCD sensor with a spectral resolution of about 1.6 nm
– The X-Y alignment (tip/tilt) of the sample is done with manual adjustment and is based on an electro-optical detector, sample alignment resolution: 0.001°.
– “Transmission Sample Holder” available for measures in transmission
– The minimum acquisition time for the entire spectral range is approximately 52 ms.
The maximum acquisition speed is approximately 20 Hz.
The typical measurement time for the entire spectrum is between 1s and 5s.
AVAILABLE TECHNIQUES
-Ellipsometric measures in reflection and transmission on a single point and on an entire area.
SAMPLES
- Sample maximum dimensions: diameter 150 mm
- Multilayer and single layer samples
USED FOR
Optical characterization of different type of film realized with several materials (semiconductors, dielectrics, polymers, organics, and metals)
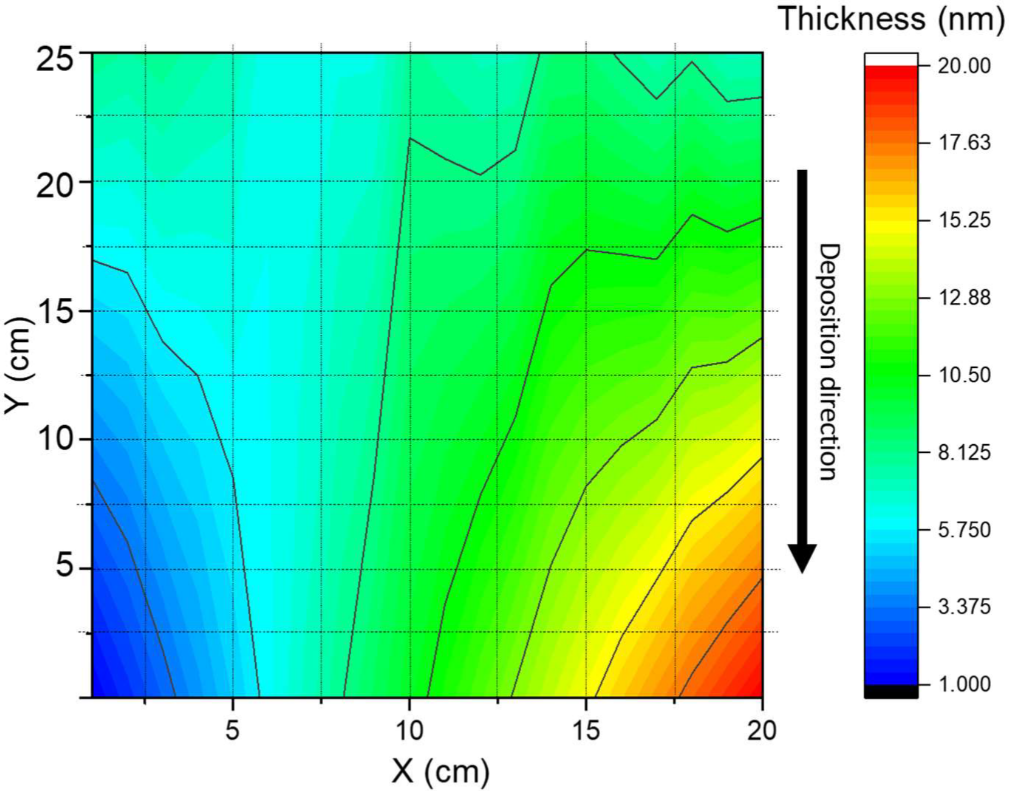
Ellipsometry statistic of PET/ITO/PTAA; 5 mg/mL concentration used. Average thickness calculated using standard deviation: 7.6 ± 0.4 nm. Tauc–Lorentz and Gaussian models were used.
Published in:
https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101980