Gas Chromatograph ion mobility spectrometer coupled with autosampler for headspace analysis
Autocampionatore HDA Autosampler HDA
Name of the contact point Rosamaria Capuano (capuano@ing.uniroma2.it) Name of the laboratory: Centro Interdipartimentale per la volatolomica
Description of the technique
Fast GC, Gas chromatograph with ion mass spectrometer detection. Coupled with a autosampler with controlled temperature
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Ionisation method: ß-radiation
Source: Tritium (3H)
Activity: 300 MBq, below the exemption limit of 1 GBq acc.to EURATOM guideline, no licence required
Column type: Multi Capillary Column (MCC) or Capillary Column (CC) – various stationary phases available
Sampling: Integrated pump plus heated electrical 6-port-valve (stainless steel), gas tight loop (1-10 mL)
Detection limit: Typically low ppbv-range
Dynamic range: 1-3 orders of magnitude
Display: Touchscreen 6.4” TFT
Communication: RS232, USB, Ethernet
Power: 100 – 240 V AC, 50-60 Hz (external) 24 V DC / 8.3A, XLR-connector (internal)
Power consumption: < 200 Watt
Dimensions: 449 x 435 x 177 mm (WxDxH)
Weight: 15,5 kg or 34,2 lb
Housing: 19” compatible, IP 20 enclosure, CE Marking
AVAILABLE TECHNIQUES
Headspace analysis
Automatic sample injection with programmable temperature
SAMPLE
Analysis of the headspace of either solid or liquid samples. To enable the use with the autosampler the sample is kept in suitable vials capped with a perforable sept. The manual use is available
USE FOR: Mainly used for volatolomics analysis. The volatolome is the volatile fraction of the metabolome of biological samples. These may be collected in-vivo (urines, saliva, plasma,…) or in-vitro from cultured cells or microorganisms. The instrument is also used to analyze the volatilome from vegetable samples and food matrices and intermediate products of industrial food processes and beverages
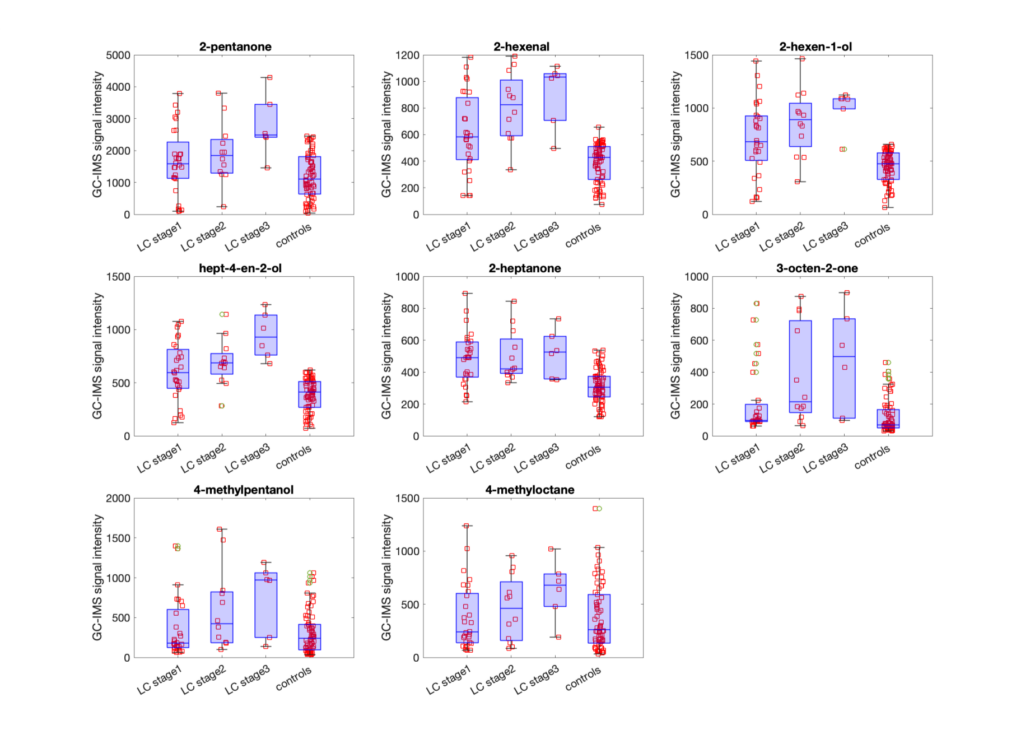
Case study 1 – Urine analysis for lung cancer diagnosis
Analysis of urines samples collected at the
European Institute of Oncology (IEO) Milan from individuals affected by lung cancer at various stages and healthy controls.
Machine learning analysis of GC-IMS data enables the diagnosis of the diseases and the identification of different stages of the disease progression.
Results published in: Gasparri et al. Journal of Breath Analysis 16 (2022) 046008.